Testosterone, often referred to as the “male hormone,” has long been associated with masculinity, virility, and strength. It plays a vital role in the development of male characteristics, influencing physical attributes, reproductive function, and even behavior.
However, the power of testosterone extends beyond stereotypes and encompasses a complex interplay between biology, psychology, and social factors. In this article, we will explore the multifaceted nature of testosterone, its effects on the human body, and its role in shaping masculinity

Understanding Testosterone
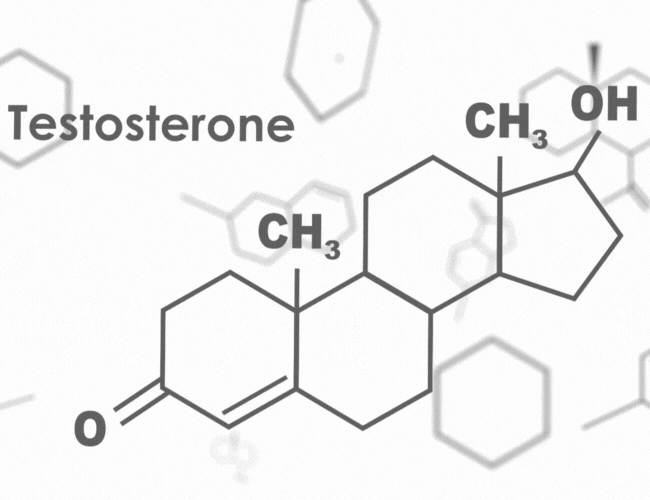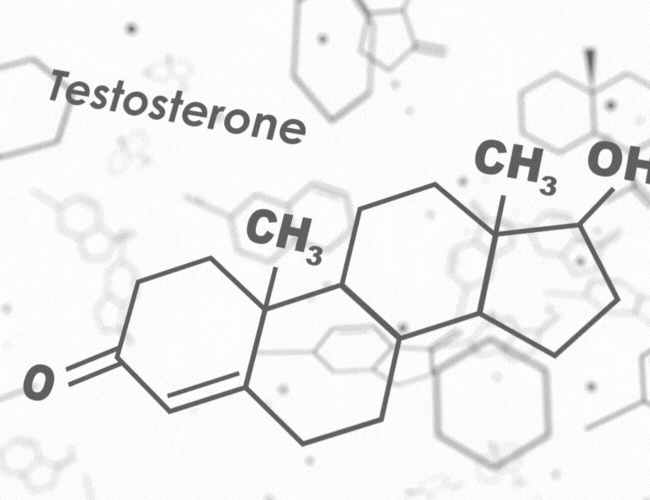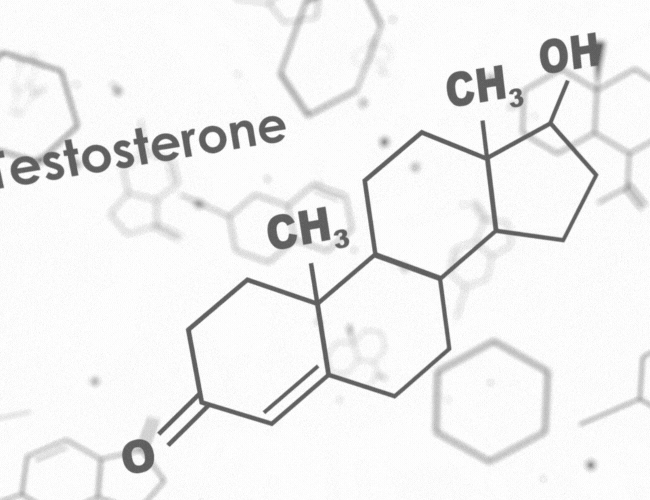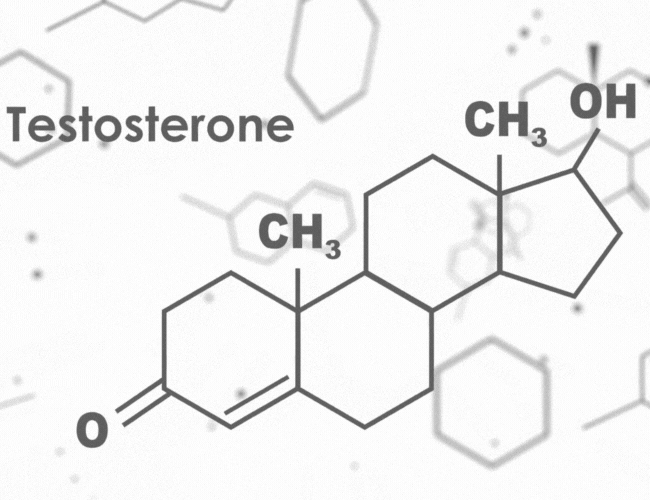
Testosterone belongs to a class of hormones called androgens and is primarily produced in the testes in males, although it is also present in smaller amounts in females. It plays a crucial role in the development of male reproductive organs during fetal development and puberty, leading to the growth of facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and increased muscle mass. Additionally, testosterone is involved in sperm production and the regulation of sexual function.
Physical Effects of Testosterone
The impact of testosterone on the male body goes beyond sexual characteristics. Testosterone influences bone density, contributing to the development of a strong skeletal structure. It also plays a role in the distribution of body fat, with higher testosterone levels typically associated with leaner body composition. Furthermore, testosterone promotes the growth of muscle tissue and helps to maintain muscle mass throughout life.
Cognitive and Emotional Influences
Beyond its physical effects, testosterone exerts influences on cognition and emotions. Research suggests that testosterone may enhance spatial and mathematical abilities, as well as contribute to risk-taking behavior. However, it is important to note that the relationship between testosterone and cognitive abilities is complex and varies among individuals.
Testosterone has also been linked to certain emotional states. Higher testosterone levels have been associated with increased self-confidence, assertiveness, and dominance. However, it is essential to avoid oversimplifying these connections, as social and cultural factors can also shape behavior and expressions of masculinity.
Testosterone and Mental Health
The relationship between testosterone and mental health is an area of ongoing research. Low testosterone levels have been associated with symptoms of depression, fatigue, and reduced motivation. Conversely, some studies have suggested a correlation between higher testosterone levels and aggressive behavior, although the link between testosterone and aggression remains complex and context-dependent.
Testosterone and Relationships
Testosterone plays a significant role in sexual desire and behavior. It influences libido and contributes to the maintenance of sexual function in both men and women.
Research suggests that testosterone levels may impact relationship dynamics, with some studies indicating that higher testosterone levels in men are associated with a greater desire for multiple partners or a higher likelihood of engaging in risk-taking behavior.
However, it is crucial to recognize that individual differences and cultural influences play a substantial role in shaping relationships.
The Impact of Lifestyle Factors
Various lifestyle factors can influence testosterone levels. Regular exercise, particularly strength training, has been shown to increase testosterone production. Sufficient sleep, a healthy diet, and stress management also contribute to maintaining optimal hormone balance. On the other hand, chronic stress, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles can lead to decreased testosterone levels.
Testosterone Supplementation and Controversies

Testosterone supplementation has become a topic of interest, particularly among aging men seeking to address symptoms associated with declining hormone levels. While testosterone replacement therapy can be beneficial for individuals with clinically low testosterone, it is essential to approach supplementation with caution. The use of testosterone without medical supervision can have unintended consequences and potential risks, including cardiovascular complications and hormone imbalances.
Moving Beyond Stereotypes
It is important to recognize that masculinity is a complex and multifaceted construct that extends beyond hormone levels. While testosterone contributes to certain aspects of masculinity, social and cultural factors play significant roles in shaping individual expressions of gender identity and behavior. Stereotypes and rigid expectations can limit the understanding and appreciation of the diverse ways in which individuals experience and express their masculinity.
Conclusion
Testosterone undeniably holds a significant influence over various aspects of male development, physicality, and behavior. It plays a pivotal role in the formation of male characteristics and affects cognition, emotions, and relationships.
However, it is vital to approach testosterone’s power with a nuanced understanding, recognizing the interplay of biology, psychology, and sociocultural factors in shaping masculinity.
By unraveling the complexities of testosterone, we can move beyond stereotypes and foster a more comprehensive understanding of the diverse experiences of individuals and their hormone profiles.


